Thermal power station (terms and translations) || Тепловая электростанция (термины и перевод)
Рубрика: Энергетика
|
Направление перевода: Англо-русский.
Тематика перевода: Энергетика
Первоисточник: Информация и рисунки для данной статьи заимствованы из Википедии: ссылка на оригинальную страницу описания.
====================================================
Translation pair: English-Russian.
Translation subject: Energy Industry
Source: All information and figures contained on this article are taken from Wikipedia: link to original description page.
|
ПРИМЕЧАНИЯ:
- В статье рассматривается один из видов тепловых электростанций (ТЭС), а именно, так называемые конденсационные тепловые электростанции (КЭС). Свое название они получили в соответствии с особенностями принципа их работы.
- Устаревшее название «ГРЭС» — государственная районная электростанция.
|
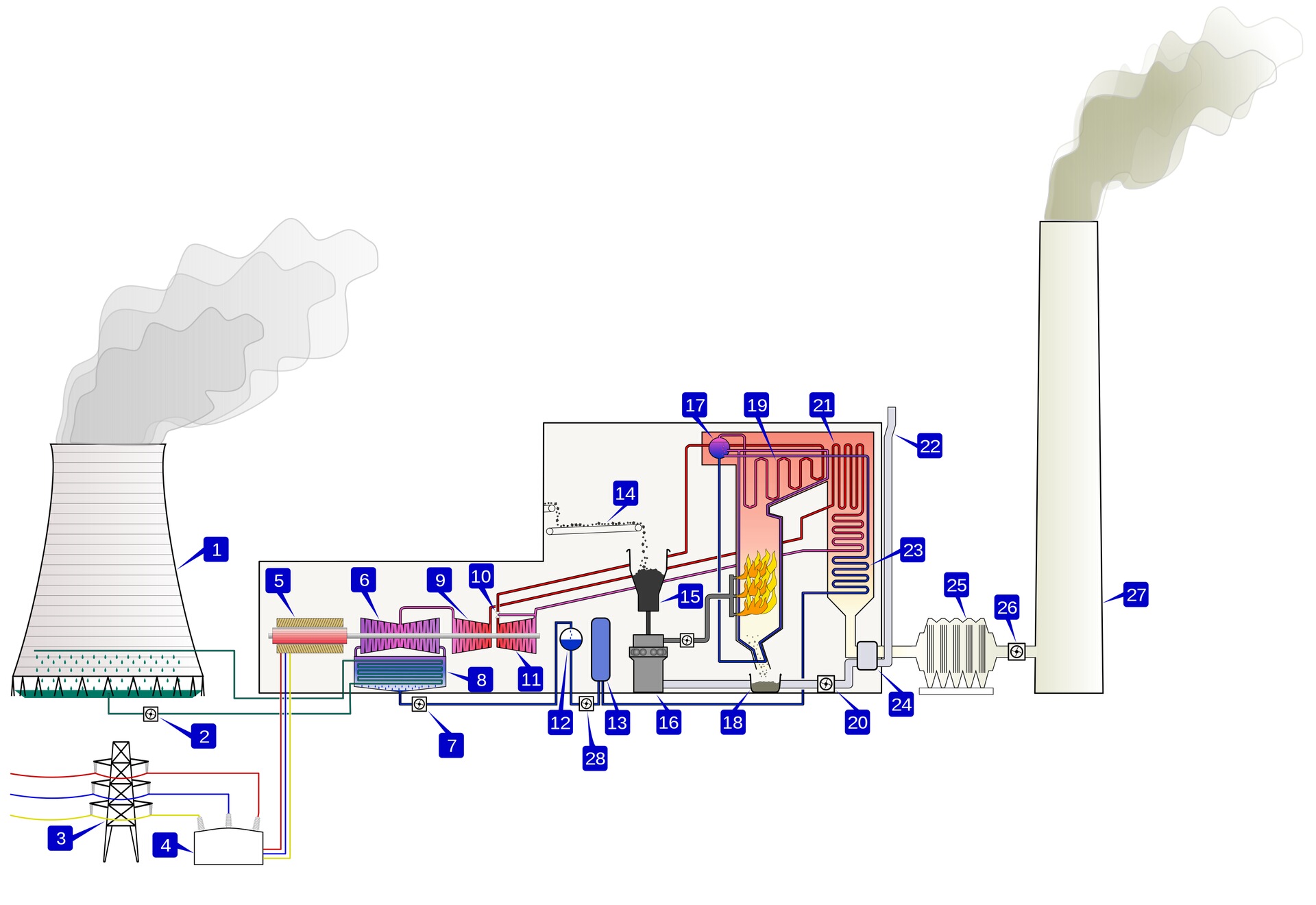 Thermal power station || Тепловая электростанция
Thermal power station || Тепловая электростанция
| № | Термин (Английский) | Перевод (Русский) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cooling tower | Градирня |
| 2 | Cooling water pump | Насос водяного охлаждения; Циркуляционный насос |
| 3 | Transmission line (3-phase) | Линия электропередачи (3-х фазная) |
| 4 | Step-up transformer (3-phase) | Повышающий трансформатор |
| 5 | Electrical generator (3-phase) | Электрогенератор; Электромашинный генератор |
| 6 | Low pressure steam turbine | Паровая турбина низкого давления |
| 7 | Condensate pump | Конденсатный насос |
| 8 | Surface condenser | Поверхностный конденсатор |
| 9 | Intermediate pressure steam turbine | Паровая турбины среднего давления |
| 10 | Steam control valve | Клапан регулировки подачи пара |
| 11 | High pressure steam turbine | Паровая турбина высокого давления |
| 12 | Deaerator | Деаэратор |
| 13 | Feedwater heater | Подогреватель питательной воды |
| 14 | Coal conveyor | Транспортёр угля |
| 15 | Coal hopper | Бункер угля |
| 16 | Coal pulverizer | Углеразмольная мельница; Мельница для измельчения угля |
| 17 | Boiler drum | Барабан котла |
| 18 | Bottom ash hopper | Шлаковый бункер |
| 19 | Superheater | Пароперегреватель; Перегреватель пара |
| 20 | Forced draught (draft) fan | Дутьевой вентилятор; Тягодутьевой вентилятор |
| 21 | Reheater | Промежуточный пароперегреватель |
| 22 | Combustion air intake | Заборник первичного воздуха; Заборник воздуха в топку |
| 23 | Economiser | Экономайзер |
| 24 | Air preheater | Предварительный воздухоподогреватель |
| 25 | Precipitator | Золоуловитель |
| 26 | Induced draught (draft) fan | Дымосос; Вытяжной вентилятор |
| 27 | Flue-gas stack | Дымовая труба |
| 28 | Feed pump | Питательный насос |
|
Coal is conveyed (14) from an external stack and ground to a very fine powder by large metal spheres in the coal pulverizer (16). There it is mixed with preheated air (24) driven by the forced draught fan (20). The hot air-fuel mixture is forced at high pressure into the boiler where it rapidly ignites. Water of a high purity flows vertically up the tube-lined walls of the boiler, where it turns into steam, and is passed to the boiler drum (17), where steam is separated from any remaining water. The steam passes through a manifold in the roof of the drum into the pendant superheater (19) where its pressure and temperature increase rapidly to around 200 bar and 570°C, sufficient to make the tube walls glow a dull red. The steam is piped to the high pressure turbine (11), the first of a three-stage turbine process. A steam governor valve (10) allows for both manual control of the turbine and automatic set-point following. The steam is exhausted from the high pressure turbine, and reduced in both pressure and temperature, is returned to the boiler reheater (21). The reheated steam is then passed to the intermediate pressure turbine (9), and from there passed directly to the low pressure turbine set (6). The exiting steam, now a little above its boiling point, is brought into thermal contact with cold water (pumped in from the cooling tower) in the condensor (8), where it condenses rapidly back into water, creating near vacuum-like conditions inside the condensor chest. The condensed water is then passed by a condensate pump (7) to a deaerator (12), then pumped by feedwater pump (28) and pre-warmed, first in a feed heater (13) powered by steam drawn from the high pressure set, and then in the economiser (23), before being returned to the boiler drum. The cooling water from the condensor is sprayed inside a cooling tower (1), creating a highly visible plume of water vapor, before being pumped back to the condensor (8) in cooling water cycle. The three turbine sets are sometimes coupled on the same shaft as the three-phase electrical generator (5) which generates an intermediate level voltage (typically 20-25 kV). This is stepped up by the unit transformer (4) to a voltage more suitable for transmission (typically 250-500 kV) and is sent out onto the three-phase transmission system (3). |
Уголь транспортируется (14) из внешней шахты и измельчается в очень мелкий порошок крупными металлическими сферами в мельнице (16). Там он смешивается с предварительно подогретым воздухом (24), нагнетаемым дутьевым вентилятором (20). Горячая воздушно-топливная смесь принудительно, при высоком давлении, попадает в котел, где быстро воспламеняется. Вода высокой чистоты течет вертикально вверх по трубчатым стенкам котла, где она превращается в пар и поступает вместе с ним в барабан котла (17), в котором пар отделяется от оставшейся воды. Пар проходит через коллектор в крышке барабана в подвесной перегреватель (19), где его давление и температура быстро возрастают до 200 бар и 570°С, достаточных для того, чтобы стенки труб светились тускло-красным цветом. Затем пар поступает в турбину высокого давления (11), первую из трех в процессе генерации электроэнергии. Клапан регулировки подачи пара (10) обеспечивает как ручное управление турбиной, так и автоматическое по заданным параметрам. Пар выпускается из турбины высокого давления как со снижением давления, так температуры, после чего он возвращается на подогрев в промежуточный пароперегреватель (21) котла.
///////////////////////////////
///////////////////////////////
///////////////////////////////
///////////////////////////////
|
Комментарии пользователей
Комментариев пока нет